Understanding Control Systems Automation Types and Their Applications
In recent years, the realm of control systems automation has become a focal point in various industries, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in operations. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global control systems market is projected to reach $29.6 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6% from 2020. This growth is largely driven by the increasing demand for process automation and the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning within control systems.
Industry experts like Dr. Emily Chen, a leading authority in automation technology, highlight the importance of understanding the different types of control systems automation, stating, "The evolution of control systems is not just about technology; it's about rethinking how we approach efficiency and productivity in every sector." This perspective underscores the critical role of control systems automation in shaping operational strategies and driving innovation across numerous applications, from manufacturing to energy management.
As we delve deeper into the various types of control systems automation and their specific applications, it becomes evident that mastering this domain is essential for organizations seeking to remain competitive in a rapidly changing market landscape. Embracing these advancements will ultimately pave the way for smarter, more responsive, and highly optimized operational frameworks.
Types of Control Systems: Open Loop vs. Closed Loop Automation
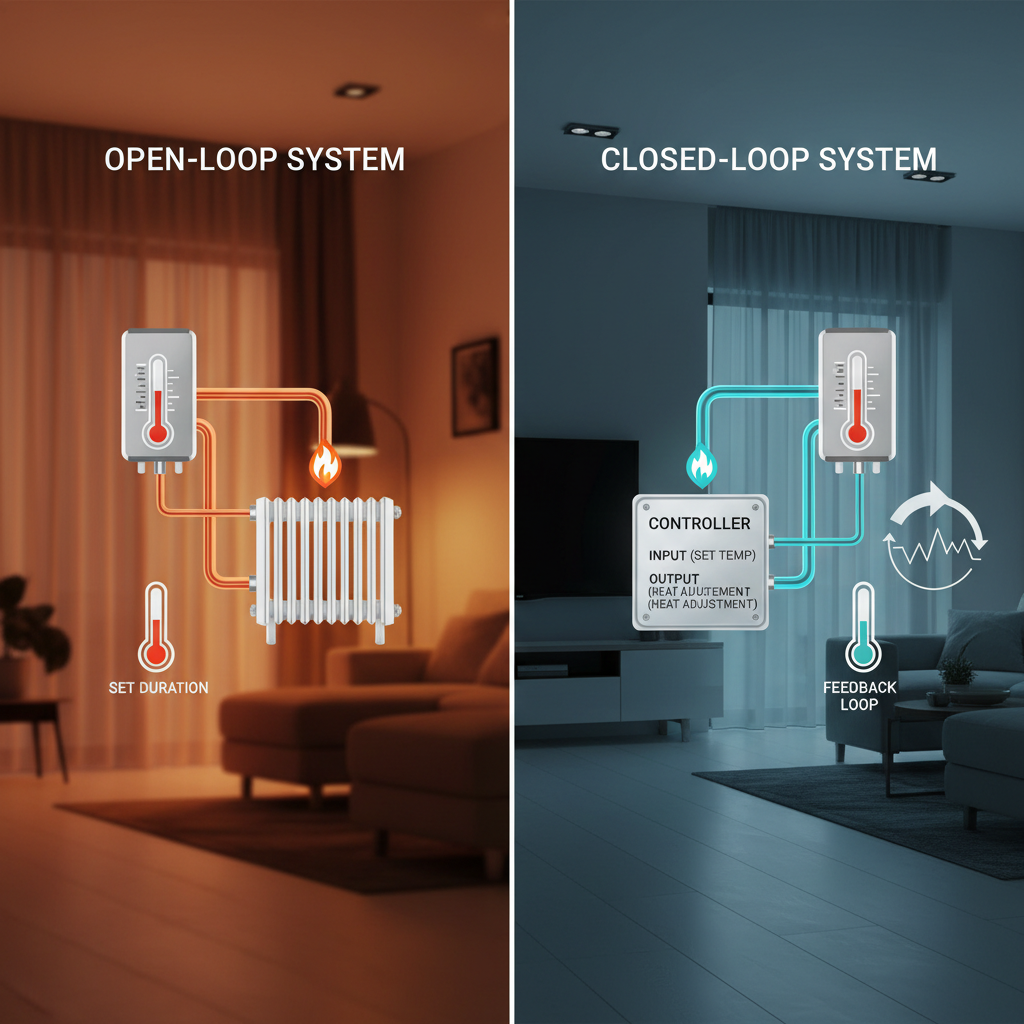
Control systems automation is essential in modern industries, and understanding the difference between open-loop and closed-loop systems is crucial for effective implementation. Open-loop systems operate without feedback; they execute a predetermined task based on input signals, but do not adjust based on the output results. For example, a simple home heating system that turns on for a set duration without sensing the actual room temperature exemplifies an open-loop control. While they are generally simpler and cost-effective, open-loop systems can be less reliable in varying conditions.
In contrast, closed-loop systems incorporate feedback mechanisms, allowing them to adjust their operations based on the output results. This type of automation continuously monitors the output and makes real-time adjustments to ensure the desired outcome. An example would be a thermostat-controlled heating system that adjusts the heating based on the current room temperature. Closed-loop systems provide higher accuracy and efficiency, making them ideal for complex processes.
Tips: When choosing between open-loop and closed-loop systems, consider the complexity of your process and the level of accuracy required. For simpler tasks with consistent conditions, an open-loop system may suffice. However, if conditions frequently change or precision is paramount, investing in a closed-loop system can enhance reliability and performance. Always assess the long-term benefits over initial costs to determine the best option for your automation needs.
Key Components of Automation Control Systems: Sensors and Actuators
Sensors and actuators are fundamental components that play a crucial role in automation control systems. Sensors are devices that detect and measure various physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, light, and motion. They convert these physical phenomena into electrical signals that can be interpreted by a control system. By providing real-time data, sensors enable automation systems to monitor the environment and make informed decisions. For instance, in an industrial setting, temperature sensors can regulate heating systems, ensuring optimal operating conditions and preventing equipment failure.
On the other hand, actuators are responsible for executing the commands from the control system. They receive signals from the control unit and convert them into physical actions, such as moving a valve, starting a motor, or adjusting a position. Common types of actuators include electric motors, hydraulic cylinders, and pneumatic devices. Their ability to perform precise movements in response to control signals makes them essential for automating processes. Together, sensors and actuators create a feedback loop, allowing for efficient and accurate operation of various applications, from manufacturing lines to smart home systems. This synergy is what enhances the overall effectiveness of automation control systems.
Understanding Control Systems Automation Types and Their Applications - Key Components of Automation Control Systems: Sensors and Actuators
| Component Type | Description | Applications | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor | A device that detects and measures physical properties. | Temperature control, pressure monitoring, motion detection. | High accuracy, response time, calibration requirements. |
| Actuator | A component that converts energy into motion. | Robotics, valve control, robotic arms. | Speed, precision, durability, control method. |
| Controller | Device that processes sensor inputs and activates actuators. | Industrial automation systems, HVAC systems. | Programmability, connectivity, logic capabilities. |
| Interface | Medium through which users interact with control systems. | Control panels, software applications. | User-friendliness, feedback mechanisms, design. |
Applications of Control Systems in Various Industries: A Sector Overview
Control systems play a crucial role in various industries by enhancing automation and improving operational efficiency. In sectors such as manufacturing, energy, and healthcare, control systems are implemented to optimize processes, reduce human error, and ensure safety. The rise of technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) is further revolutionizing how these systems function. For instance, AI can enable predictive maintenance, allowing organizations to identify potential failures before they occur, thus minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
The PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) market, which has evolved from relay control technology, is experiencing significant developments. Different categories of PLCs—small, medium, and large—are tailored to specific industrial needs, contributing to automation and efficiency across various applications. With the increasing demand for smart, networked solutions, sectors such as electronic information manufacturing and energy are at the forefront of this transformation.
The integration of advanced industrial control solutions is paving the way for greater automation, redefining operational paradigms in industries deep into the digital economy era. As sectors continue to embrace innovations in control systems, they usher in improved productivity and higher standards of quality across the board.
Digital Transformation in Control Systems: Trends and Innovations
Digital transformation is reshaping control systems across industries, with a notable emphasis on enhancing operational efficiency and driving innovation. By 2025, organizations are expected to leverage digital technologies significantly, as evidenced by the McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2025, which predicts that advances in artificial intelligence, automation, and real-time data analytics will revolutionize traditional practices. This transformation is not only about adopting new technologies but also about creating a culture that embraces change and prioritizes human-centered innovation.
Tips for success in digital transformation include investing in comprehensive training programs that empower employees to utilize new tools effectively. It's essential to establish clear metrics to evaluate the impact of these technologies on productivity and operational risk. For example, businesses in the mining sector anticipate enhanced productivity levels as they integrate digital systems that enable better data management and decision-making processes.
As we navigate this digital landscape, organizations must focus on aligning their transformation strategies with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles. Emphasizing sustainability and ethical practices not only drives innovation but also aligns with consumer expectations in a digitally connected world.
Best Practices for Implementing Control Systems Automation Effectively
When implementing control systems automation, adhering to best practices is crucial for maximizing efficiency and minimizing risks. A study by McKinsey & Company highlights that organizations that effectively implement automation can improve productivity by 20-25%. This improvement is often achieved through a systematic approach that includes thorough needs assessments, selection of appropriate technologies, and continuous integration into existing systems. Successful automation requires not only robust technology but also alignment with the organization's strategic goals.
Another vital practice is engaging stakeholders throughout the entire automation process. According to a report from Deloitte, companies that involve employees in the automation implementation processes experience a 30% higher acceptance rate of new technologies. This involvement ensures that all potential barriers are addressed, and it promotes a culture of innovation. Furthermore, regular training sessions and feedback mechanisms should be established to keep the workforce informed and adaptable. By focusing on both technological and human factors, organizations can harness the full potential of control systems automation, driving substantial improvements in performance and operational efficiency.
Control Systems Automation Types and Their Applications
This chart illustrates various types of control systems automation and their respective application counts in industrial settings. PID Control leads with the highest number of applications, followed by Fuzzy Logic and Neural Networks, indicating their prevalent use in automation processes.