Understanding Control Systems Automation for Enhanced Efficiency and Performance
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the significance of control systems automation cannot be overstated. As organizations strive for enhanced efficiency and performance, the integration of advanced control systems becomes paramount. Experts in the field, such as Dr. Emily Roberts, a renowned automation specialist, assert, “The future of industry relies heavily on the implementation of intelligent control systems that enhance productivity and streamline operations.” This assertion underscores the transformative impact that control systems automation has on various sectors, enabling them to operate with unprecedented precision and effectiveness.
Control systems automation encompasses a broad range of technologies and methodologies designed to monitor and control processes with minimal human intervention. By harnessing the power of automation, industries are able to reduce operational costs, improve safety, and achieve higher quality outputs. As automation technologies evolve, the potential for control systems to drive efficiency becomes even greater, prompting organizations to invest in adaptive systems that can respond dynamically to changing conditions.
The journey toward optimizing performance through control systems automation is not without its challenges. However, as Dr. Roberts emphasizes, the rewards far outweigh the hurdles. The adoption of robust control systems can lead to significant advancements in operational capabilities, ultimately positioning organizations to thrive in an increasingly competitive market. As we delve deeper into this subject, we will explore the various facets of control systems automation and its pivotal role in shaping the future of industry.

Definition and Components of Control Systems Automation
Control systems automation refers to the technological processes that manage and govern the behavior of dynamic systems. At its core, it encompasses the integration of hardware and software designed to oversee machines, processes, and systems with minimal human intervention. By establishing rules and algorithms, control systems can efficiently respond to changes in environmental conditions or operational demands, thereby enhancing overall performance.
The primary components of control systems automation include sensors, controllers, and actuators. Sensors act as the eyes and ears of the system, gathering real-time data about variables such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates. This information is then transmitted to the controller, a critical component that processes the data and makes informed decisions based on predetermined algorithms.
Finally, actuators serve as the muscles of the system, executing the commands issued by the controller to adjust output variables and maintain desired performance levels. Together, these components create a closed-loop system that continuously monitors and adjusts to optimize efficiency and effectiveness in various applications, from industrial manufacturing to smart home technologies.
Benefits of Control Systems Automation for Efficiency Improvements
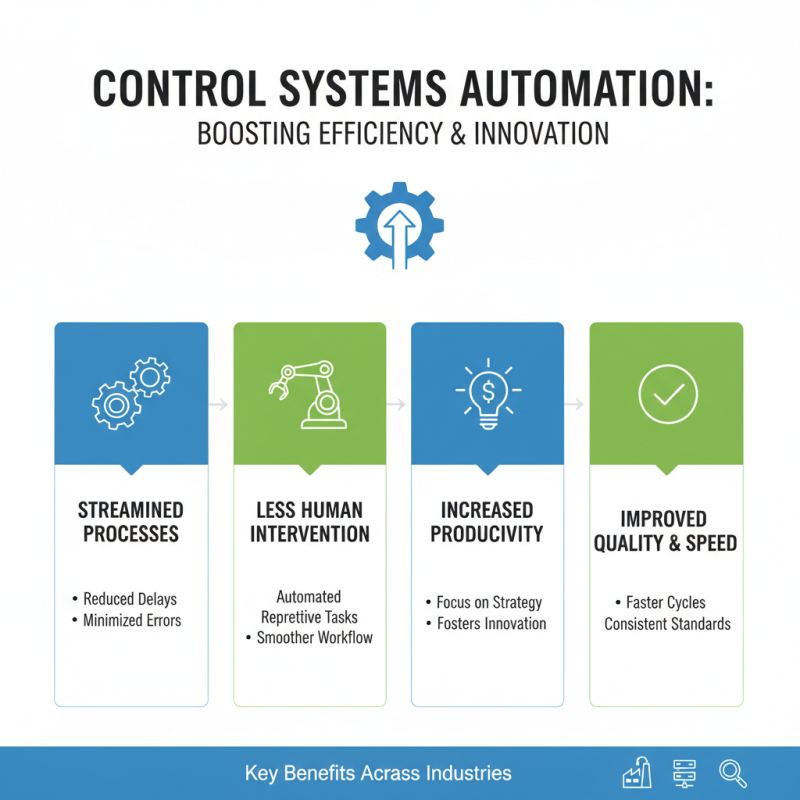
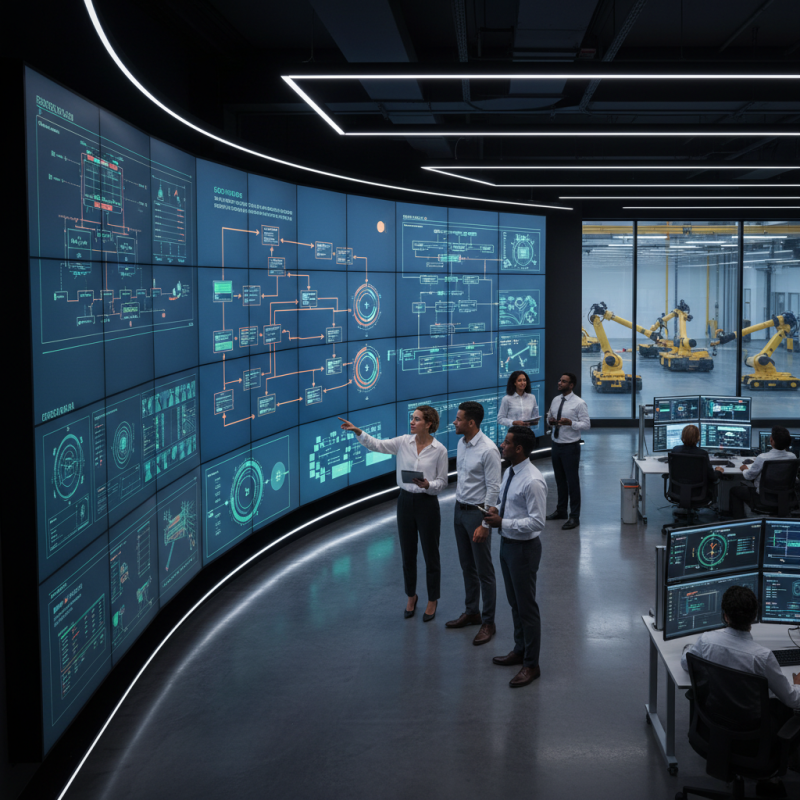
Control systems automation plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency across various industries by streamlining processes and reducing human intervention. By integrating automated control systems, organizations can minimize operational delays and errors, leading to a smoother workflow. The automation of repetitive tasks allows employees to focus on more strategic activities, fostering innovation and productivity. This transition not only speeds up production cycles but also improves product quality, as automated systems consistently adhere to established standards and protocols.
Moreover, the benefits of control systems automation extend to significant cost savings. By optimizing resource allocation and reducing waste, businesses can achieve substantial reductions in operational costs. Enhanced monitoring and real-time data analysis enable proactive decision-making, which helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate into costly problems. As a result, companies can maintain high levels of efficiency while also improving their bottom line. In a competitive market, these efficiency improvements can provide a significant advantage, positioning organizations for sustained growth and success.
Types of Control Systems Used in Automation Processes
Control systems play a pivotal role in automation processes across various industries, enhancing efficiency and performance. The primary types of control systems utilized in automation include open-loop and closed-loop systems.
Open-loop control systems operate without feedback, executing commands without any adjustment based on the output results. For instance, in a manufacturing assembly line, an open-loop system may control a conveyor belt that functions continuously without measuring the exact output or making real-time adjustments. According to a market report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for open-loop control systems is expected to reach $2.5 billion by 2025, driven largely by their simplicity and cost-effectiveness in less complex applications.
In contrast, closed-loop control systems utilize feedback mechanisms to continuously monitor and adjust the output based on desired performance criteria.
These systems are critical in environments where precision is paramount, such as in temperature control processes or robotic automation. The International Federation of Robotics estimates that closed-loop systems account for over 60% of advanced automation implementations, illustrating their growing importance in sectors requiring high levels of accuracy and reliability. By adjusting operational parameters in real-time, closed-loop systems not only improve overall productivity but also reduce waste, playing a significant role in the ongoing development of smart manufacturing processes.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Control Systems Automation
Implementing control systems automation presents several challenges that organizations must navigate to achieve enhanced efficiency and performance. One of the primary obstacles is the integration of new technologies with existing systems. Legacy systems often lack compatibility with modern automation tools, leading to disruptions in operations if not managed properly. To address this issue, organizations can adopt a phased approach to implementation, allowing for gradual integration and minimizing operational downtime. Moreover, thorough training programs for employees are essential to ensure they are well-equipped to work alongside newly automated systems.
Another critical challenge is the management of data security and privacy concerns. As control systems increasingly rely on connected devices and cloud services, the risk of cyber threats escalates. Organizations must invest in robust cybersecurity measures and regularly update their security protocols to protect sensitive data. Additionally, establishing clear policies around data usage and access can help mitigate risks. With these solutions in place, companies can not only streamline their operations through automation but also foster a secure environment that supports ongoing innovation and productivity.
Control Systems Automation Impact on Efficiency
This bar chart illustrates the impact of control systems automation on operational efficiency. The data shows a significant improvement in efficiency, from 65% before automation to 85% after implementation, highlighting the benefits of integrating automation in control systems.
Future Trends in Control Systems Automation for Enhanced Performance
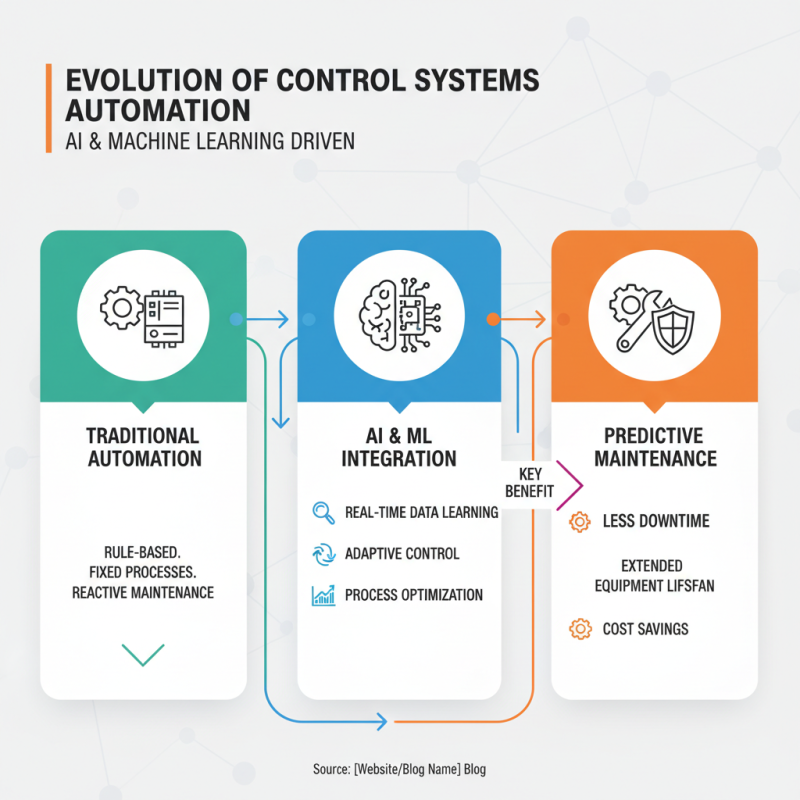
The landscape of control systems automation is experiencing rapid evolution, driven by advancements in technology and an increasing demand for efficiency. One of the most notable trends is the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms. These technologies enable systems to learn from data in real-time, adapt to varying conditions, and optimize processes. For instance, predictive maintenance facilitated by AI can preemptively address equipment failures, significantly reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of machinery.
Another emerging trend in control systems automation is the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. As more devices become interconnected, the ability to collect and analyze vast amounts of data is transforming how control systems operate. IoT-enabled sensors can provide instant feedback on system performance, leading to more informed decision-making and enhanced operational strategies. This connectivity not only improves efficiency but also facilitates a more comprehensive approach to performance monitoring and management, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to any issues that may arise in their processes.
Furthermore, as organizations continue to prioritize sustainability, automation systems are increasingly being designed with energy efficiency in mind. Innovations in energy management within control systems can help in minimizing waste, thus contributing to lower operational costs and a reduced ecological footprint. These future trends signify a shift towards more intelligent, adaptive, and environmentally conscious control systems, paving the way for enhanced performance across various industries.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Industrial Automation Software for Your Business
-

Top Industrial Automation Solutions to Improve Efficiency and Productivity
-
Top Automation Control Trends to Watch in 2025 for Enhanced Efficiency
-

Understanding Control Systems Automation Types and Their Applications
-
2025 Top 10 Automation Equipment Trends Driving Industry Growth and Efficiency